题目
题目描述
A,B两个国家正在交战,其中A国的物资运输网中有$N$个中转站,$M$条向道路。设其中第$(1\leq i\leq M)$条道路连接了$v_i,u_i$两个中转站,那么中转站$v_i$可以通过该道路到达$u_i$中转站,如果切断这条道路,需要代价$c_i$。
现在B国想找出一个路径切断方案,使中转站$s$不能到达中转站$t$,并且切断路径的代价之和最小。
小可可一眼就看出,这是一个求最小割的问题。但爱思考的小可可并不局限于此。现在他对每条单向道路提出两个问题:
问题一:是否存在一个最小代价路径切断方案,其中该道路被切断?
问题二:是否对任何一个最小代价路径切断方案,都有该道路被切断?
现在请你回答这两个问题。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行有$4$个正整数,依次为$N,M,s,t$。
第$2$行到第$(M+1)$行每行$3$个正整数$v,u,c$表示$v$中转站到$u$中转站之间有单向道路相连,单向道路的起点是$v$, 终点是$u$,切断它的代价是$c(1\leq c\leq 100000)$。
注意:两个中转站之间可能有多条道路直接相连。 同一行相邻两数之间可能有一个或多个空格。
输出格式:
$M$对每条单向边,按输入顺序,依次输出一行,包含两个非$0$即$1$的整数,分别表示对问题一和问题二的回答(其中输出$1$表示是,输出$0$表示否)。 同一行相邻两数之间用一个空格隔开,每行开头和末尾没有多余空格。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
6 7 1 6
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 4 4
2 5 1
3 5 5
4 6 2
5 6 3
输出样例#1:
1 0
1 0
0 0
1 0
0 0
1 0
1 0
说明
测试数据规模如下表所示
| 数据编号 | N | M | 数据编号 | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 50 | 6 | 1000 | 20000 |
| 2 | 20 | 200 | 7 | 1000 | 40000 |
| 3 | 200 | 2000 | 8 | 2000 | 50000 |
| 4 | 200 | 2000 | 9 | 3000 | 60000 |
| 5 | 500 | 20000 | 10 | 4000 | 60000 |
题解
似乎有几个性质:
- 1.残余网络中有剩余流量的边一定不在最小割中
如果有剩余流量的话肯定还有更优解
如图:
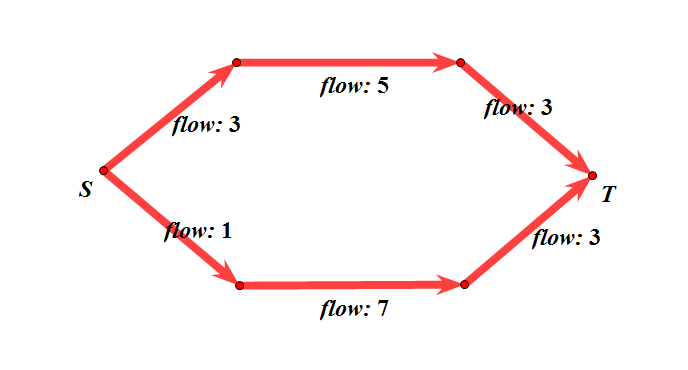
最小割为$4$,容量为$5$的边有剩余流量,它不在最小割里
- 2.残余网络中一条边(满足性质$1$)的首尾还能相互到达,那么这条边不满足条件$1$
我个人理解是一边的两点还能相互到达,说明它们在割后的同一点集合中
连接它们的边就肯定不是最小割方案,反之连接它们的边就肯定在某个最小割方案中
- 3.在残余网络中一边(满足性质$1$)的首尾分别与$S$和$T$在一个强连通分量中,那么这条边满足条件$2$
很好证明吧……
你如果不割这条边,最大流(即最小割)肯定得改变
性质$2,3$都是在性质$1$的基础上进行的,性质$2$不满足性质$3$肯定也不满足
至于是否联通,用$Tarjan$判断就行了我想用并查集失败了
代码
# include<iostream>
# include<cstdio>
# include<cstring>
# include<queue>
# include<stack>
# define ini inline int
# define inv inline void
# define inb inline bool
using namespace std;
const int MAX=4e3+1,inf=1e8;
struct p{
int fr,x,y,dis;
}c[MAX<<5];
int n,m,s,t,num,TOT,ans,cnt;
int h[MAX],d[MAX],col[MAX],dfn[MAX],low[MAX];
bool use[MAX];
stack<int> st;
ini read()
{
int x=0;
char ch=getchar();
while(!isdigit(ch)) ch=getchar();
while(isdigit(ch))
{
x=x*10+ch-48;
ch=getchar();
}
return x;
}
inv add(int x,int y,int dis)
{
c[num].fr=y,c[num].x=h[y],c[num].y=x,c[num].dis=0,h[y]=num++;
c[num].fr=x,c[num].x=h[x],c[num].y=y,c[num].dis=dis,h[x]=num++;
}
inb bfs()
{
queue<int> qu;
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
d[s]=1;
qu.push(s);
while(!qu.empty())
{
int tt=qu.front();
qu.pop();
for(int i=h[tt];i;i=c[i].x)
if(!d[c[i].y]&&c[i].dis)
{
d[c[i].y]=d[tt]+1;
qu.push(c[i].y);
}
}
return d[t];
}
int dfs(int x,int dix)
{
if(x==t||!dix) return dix;
int sum=0;
for(int i=h[x];i;i=c[i].x)
if(d[c[i].y]==d[x]+1&&c[i].dis)
{
int dis=dfs(c[i].y,min(dix,c[i].dis));
if(dis)
{
sum+=dis;
dix-=dis;
c[i].dis-=dis;
c[i^1].dis+=dis;
if(!dix) break;
}
}
if(!sum) d[x]=-1;
return sum;
}
inv dinic()
{
while(bfs()) dfs(s,inf);
}
void tarjan(int x)
{
dfn[x]=low[x]=++cnt;
use[x]=1;
st.push(x);
for(int i=h[x];i;i=c[i].x)
if(c[i].dis)
if(!dfn[c[i].y])
tarjan(c[i].y),low[x]=min(low[x],low[c[i].y]);
else if(use[c[i].y])
low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[c[i].y]);
if(low[x]==dfn[x])
{
ans++;
int tt=-1;
while(tt!=x)
{
tt=st.top();
st.pop();
col[tt]=ans;
use[tt]=0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read(),s=read(),t=read();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int x=read(),y=read(),dis=read();
add(x,y,dis);
}
dinic();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
for(int i=1;i<num;i+=2)
{
if(c[i].dis)
{
printf("0 0\n");
continue;
}
if(col[c[i].fr]==col[c[i].y])
printf("0 ");
else printf("1 ");
if(col[c[i].fr]==col[s]&&col[c[i].y]==col[t])
printf("1\n");
else printf("0\n");
}
return 0;
}